Throughout the Ukraine War, countless nations have been undeniably affected. Ukraine has lost innumerable soldiers, civilians, and infrastructure, Russia’s economy has been hit with massive unemployment due to western sanctions, and many other countries have had to confront Russia-Ukraine war inflation, especially regarding food. However, according to many international bodies ╌ including the World Bank ╌ three countries have suffered the most due to inflation: Lebanon, Zimbabwe, and Venezuela. Tragically, the countries that are suffering most from this war are the same ones facing both long-standing economic problems and sudden occurrences of crises. Crises that stem from economic and political mismanagement by policymakers and politicians.

Role of inflation in exacerbating inequality
The Russian invasion of Ukraine has continued to cause global supply chain disruptions. As a result, the prices of essential commodities such as fuel and food have increased globally. For instance, both Russia and Ukraine account for almost one-third of global wheat exports. The war has caused shortages that have increased food insecurity due to the soaring food prices. Most affected are poor countries that are already grappling with other issues such as climate change.
Russia-Ukraine war inflation: Impact on Lebanon
According to the World Bank Group, Lebanon is one of the countries that Russia-Ukraine war inflation hit hardest. In August this year, the World Bank estimated that food inflation in Lebanon increased by around 122% in real terms. Russia-Ukraine war inflation has further damaged the economy. This means that for households to be able to afford a decent meal that they enjoyed before, real wages have to increase equally. Sadly, this has not been the case. The food grain blast in Beirut two years ago is the root cause of Lebanon’s food insecurity issues. However, the Ukraine crisis has made it more difficult for Lebanon to provide affordable food to its millions of citizens and other refugees seeking asylum. In late September, Lebanon received it’s first Ukrainian grain shipment under a UN backed deal. The shipment meant to prevent a food crisis despite the negative effects of the war.
Russia-Ukraine war inflation: Impact on Zimbabwe
This place used to be packed around this time. From 5am we were busy. Now there is no one.
Simba Muchingami, Zimbabwean baker in an Aljazeera interview in September 2022.
Zimbabwe follows closely behind Lebanon in having to bear a large portion of the damage of the war. Having already suffered the damaging effects of the hyperinflation of 2008, Zimbabwe is not unfamiliar with unprecedented economic declines. However, Zimbabwe faces problems much worse and wider in scale than before. One of its biggest problems is the severely lower levels of grain able to be imported. Zimbabwe relies on many countries to import wheat. However, due to grain prices rising, bread prices have skyrocketed as well. Also, inflation spiked, adding even more to price rises of not only grain, but other commodities. To add, climate change has fueled Zimbabwe’s food crisis, and droughts have hindered agriculture in parts of the country.
Inflation: Zimbabwe vs Germany
In stark contrast, developed countries are not only less affected by the effects of the war, but actually performing quite well. For example, Germany has had to confront an energy crisis due to its historic dependence on Russian oil and gas. However, its citizens, have greater protection from price shocks than Zimbabweans. The German government secured $65 billion in September 2022 to cushion the blows to its economy, due in large part to EU sanctions on Russian oil and gas. While it will not solve the inevitable energy shortages that it and Europe at large will face, its citizens will not feel as much pressure from price rises as Zimbabweans.
Inflation in Venezuela
According to the Fraser Institute Economic Freedom of the World Report 2022, Venezuela ranks last among 165 countries with a score of 3.32. Economic mismanagement in Venezuela has caused more than a decade of pain and suffering to its citizens. While the country is not new to runaway inflation, multiple crises happening concurrently have made the situation worse in the country. The Ukraine War has made it more difficult for Venezuelans as food inflation bites.
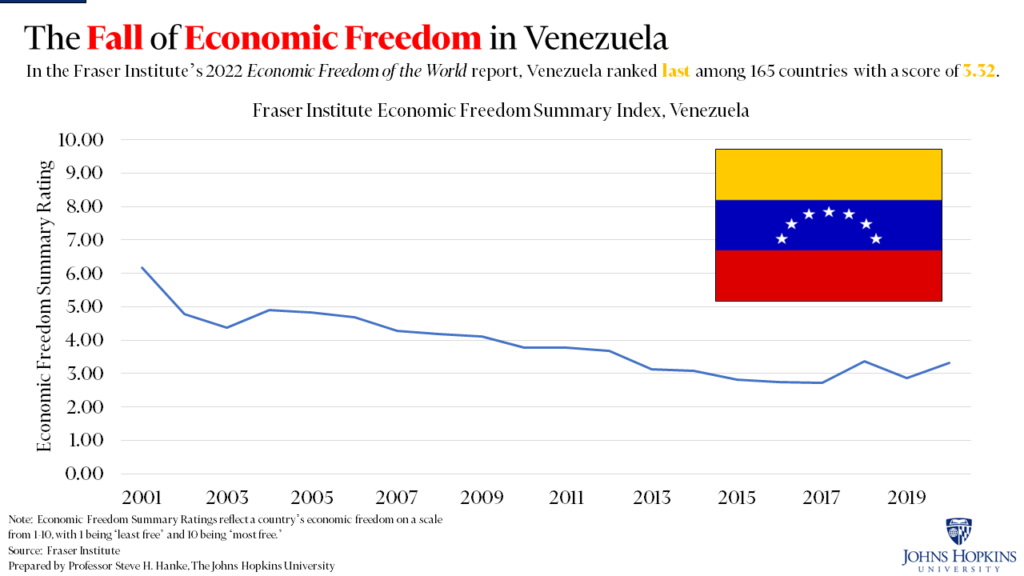
Venezuela’s action on inflation
To combat food inflation, the government has tried to intervene by reaching out to the private sector and producers and negotiating on prices of essential commodities with the aim of keeping them low. This is being done with the fresh memory of the economic contraction caused by price caps that former present Hugo Chavez imposed, which affected production levels since producers were just not willing to produce goods and services at such prices triggering economic downturns. Even with this effort, millions of refugees have been leaving Venezuela with the total count being around 6.8 million people since 2015.
Spill-over effect of fighting inflation in the United States
To keep inflation at a low level, the US Federal Reserve (Fed) has continued to raise the benchmark rate, the most recent one being on Wednesday, the 21st of September when the Fed raised the benchmark rate by three-quarters of a percentage point even amid recession fears. For emerging economies, this means that there might be a huge capital outflow from their economies to the US weakening their currencies.
Analysis of impact on developing countries
The dollar has been gaining against other currencies, especially after the hike in the Fed benchmark rate. This means more debt servicing costs for poor countries which have in the past relied on dollar-denominated loans to finance activities, especially capital-intensive ones such as building roads and other transport networks. And therefore, as inflation continues to bite and fiscal space continues to shrink as a result of other macroeconomic factors, it is important for the most affected countries to be offered financial and material support to help them cope with these overlapping crises.
Russia-Ukraine war inflation: Humanitarian effort to help the most vulnerable
Since the onset of the war, humanitarian agencies and other organizations have made efforts to help alleviate the suffering of the most vulnerable people. They have directed their support to Ukraine and other emerging economies. Because they are not self-reliant, the war thus impacts them most. For instance, the World Bank Group ( WBG) organized a $925 million package for Ukraine to help with the continuation of government activities, pay wages and salaries, and offer relief for the most vulnerable.
Recommended UN actions
The United Nations (UN) has continued to call on governments and international financial institutions to intervene through debt relief programs that would enable poor countries to pay for energy subsidies and other commodities. For continents like Africa where the poor spend most of their income on energy and food, governments have initiated different subsidy programs focused on fertilizers and fuel to cushion their citizens in the short term as they work on more sustainable long-term solutions.
Conclusion
It is, therefore, necessary for more help to be offered to countries that are hardest hit as a result of the conflict. More money and other forms of humanitarian aid need to be deployed to ease the burden of people in the most vulnerable countries. This will ensure people can afford the basic needs – food, shelter, and clothing so as to lead decent lives that all human beings deserve.
IVolunteer International is a 501(c)3 tech-nonprofit registered in the United States with operations worldwide. Using a location-based mobile application, we mobilize volunteers to take action in their local communities. Our vision is to create 7-billion volunteers. We are an internationally recognized nonprofit organization and are also a Civil Society Associated with the United Nations Department of Global Communications. Visit our profiles on Guidestar, Greatnonprofits, and FastForward.


